![]()
Do you remember those days with old-school Google search results? Whatever you searched, you received that austere list of ten blue links. Now, when you Google something relatively popular, you have a feeling you have become a part of a Brazilian carnival. Visual delight. Eyes cannot choose where to look at. So many forms, so many suggestions.
While users are happily exploring their new and newly upgraded search result options, we have to understand which search results can bring in some serious traffic, and what should be done to achieve it (and whether it is worth it at all).
I have put up a visualization guide to surgically examine major Google search results for their potential:
![]() Click for a full version of the image
Click for a full version of the image
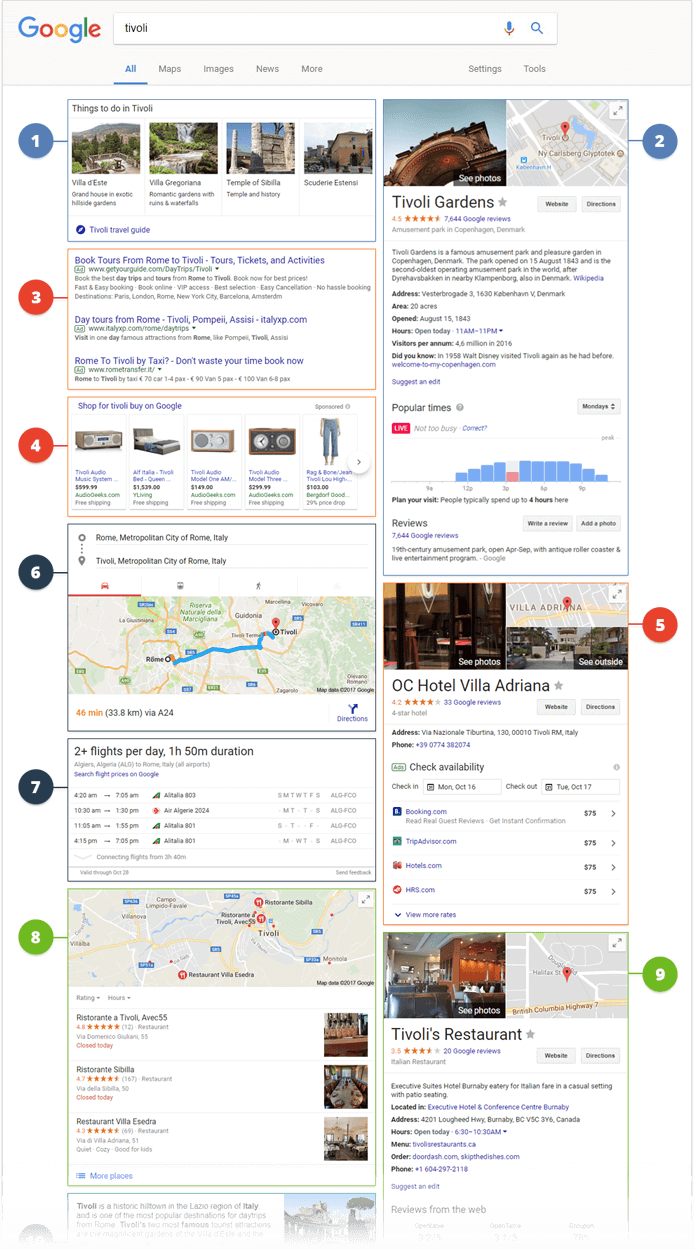
This page is, of course, artificially compiled, but it consists of real Google results. I’ve identified 7 major types of results, each having subtypes.
Knowledge graph results
Travel box
Local results
Featured snippets
Organic search results
Vertical search results
I invite you to explore these search result types and their distinct features as well as the opportunities for SEO. Let’s roll.
Knowledge Graph Results.
1. Carousel
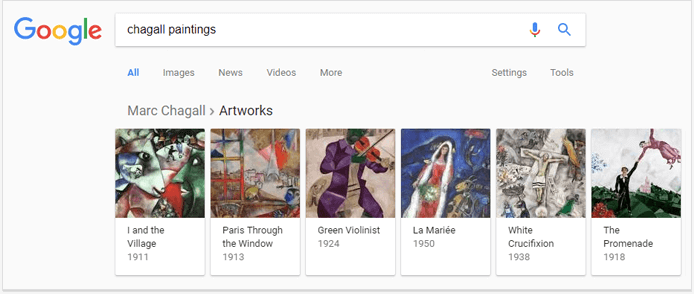
As a rule, Google returns results in carousel to non-commercial, informational queries to satisfy searcher’s intent for a selection of options.
Google has recently added a new type of carousel that allows the searcher to filter the results of a particular category:
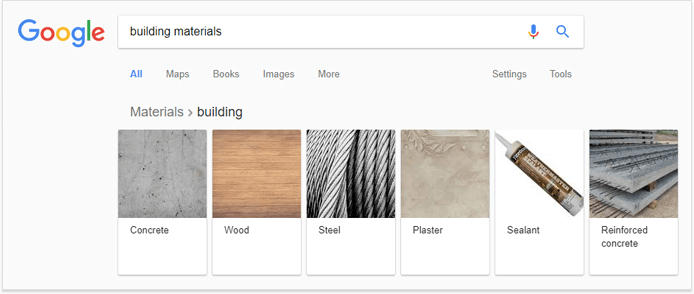
It seems that there is no direct traffic or SEO advantage that you can get from the current carousel representations. The carousel listings don’t include links to sites; clicking on one of them will simply get you to a new search results page.
2. Brand Knowledge Graph panel
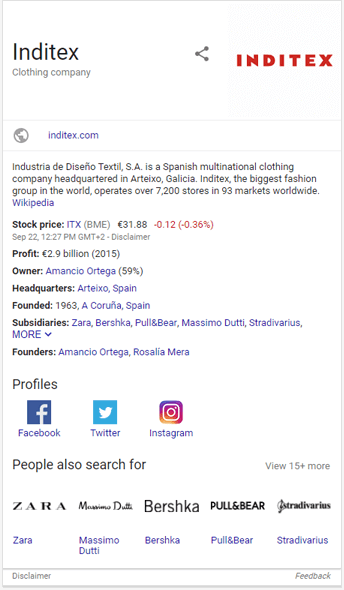
The Knowledge Graph panel is usually triggered by navigational, primarily branded queries — shops, books, movies, music bands, etc. The current version of the panel consists of the name of the company, a business type, a logo, a link to the company’s site, a description, a list of the entity’s social profiles, and a “People also search for” section.
This search result type can be very powerful in terms of traffic and brand authority — it attracts searchers’ attention and serves as a strong indicator of the company’s trustworthiness.
I should say outright — there is no sure way to get your brand to a Knowledge Graph panel. However, we know exactly what resources Google uses for its Graph. So if you follow the steps listed below, you have more chances to flash your panel to the world.
1. Get on Wikidata.
Google gets some info from Wikidata, a knowledge base operated by Wikimedia. It is easy to create an entry there — you just have to specify a few details about your business. It can be a great starting point if you plan to get an entry in Wikipedia. Check out a guide to Wikidatato get you started.
2. Get a Wikipedia article.
Wikipedia is a hard worker for the Knowledge Graph: company’s descriptions and official website addresses almost always come from there. If you consider creating an article about your company for Wikipedia, you can do it yourself or hire an experienced, trusted Wikipedia editor (there are lots of white-hat companies available to choose from). Make sure to include a link to your Wikidata entry in your article, as this can boost your chances of getting the article approved.
3. Use schema markup for organizations on your homepage.
Schema markup is a markup based on the microdata specification, which is invisible to visitors, but helps search engines to understand the page better. For your business site’s homepage, it is highly recommended to use the organization type of markup. Make sure to specify your logo, contact info, social profiles, Wikidata, and Wikipedia pages — this is the information that Google will most likely pull for the Knowledge Graph. Check Google’s instructions on customizing your markup elements.
4. Have your social media accounts verified.
If Google cannot find your official site address, or if your website does not use structured data markup, it can still display a Knowledge Graph panel for your business. However, to identify your social profiles correctly, it needs them verified by the social platforms — a blue verified badge next to the account name.
Otherwise, it can pull regional or unofficial versions of your accounts, or altogether fail to display any. Each social network has their own guidelines for getting accounts verified. Here are some great tips for verifying your profiles on Twitter, Facebook, YouTube & Google+, and Instagram.
5. Request a change from Google.
If you already have a Knowledge Graph listing, and there are some things that are not correct or need some update, you can either get in touch with Google and ask them to make changes, or you can do the editing yourself if you are an official website representative. Once the change has been made, Google will check it for accuracy and send a confirmation email to the user. There is also an indirect option of editing your Knowledge Graph result — try to optimize the sources that provide for your panel — Wikidata and Wikipedia.
Fire up SEO PowerSuite’s Rank Tracker, create a project for your website if you do not have one, or open an existing project, and by going to Preferences > Rank Checking Mode, make sure that Track organic results only box is unchecked, and the Track multiple results for keyword box is checked. Once you’ve done this, SERP features will be tracked along with the regular organic results every time you check rankings.
Once you have refreshed your rankings by selecting all or any particular keywords and clicking Check Rankings, in the Google SERP Features column you will see different kinds of icons that stand for various SERP features (if any). When your keyword got a Knowledge Graph result, it will look like this:
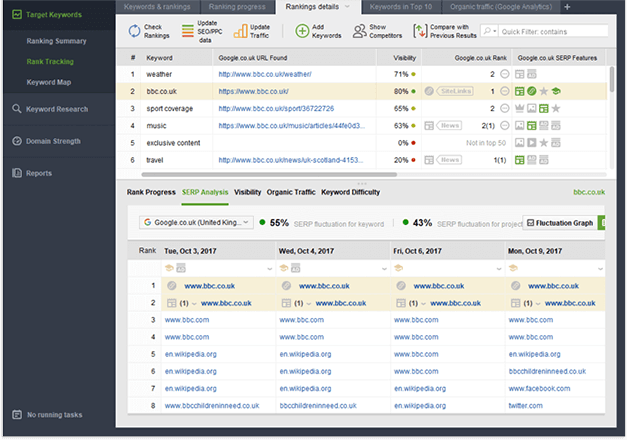
When the “square academic cap” icon is grey, it means that there is a Knowledge Graph on this page for your keyword, but the result is not yours. But when it is green — you‘ve got it!
You can also hover your mouse over your rank and click on the arrow to see what the actual SERP with this feature looks like. Plus, if your website was found on the SERP more than once, you will see the three dots in your rank, by clicking which you will summon all the results.
Ads.
3. AdWords ads
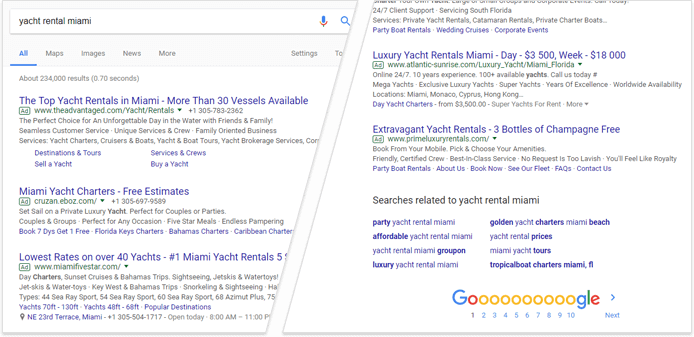
AdWords Ads are currently displayed in blocks either above or below the organic search results with a “Sponsored” disclaimer. They can appear across all kinds of Google result pages, for any type of queries, whenever Google believes there is a shopping match.
Easy-peasy, start an AdWords account and choose a suitable ad format.
4. Google shopping
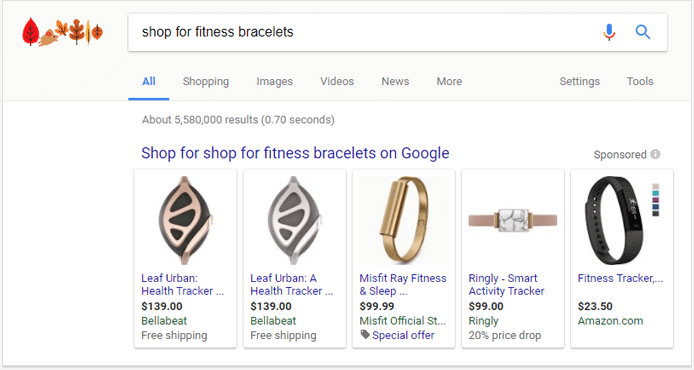
Currently, paid shopping results appear as blocks of product images and links either to the right of the organic listings or above them. This type of search results is usually displayed for queries with strong commercial intent. It shows the most crucial info of a product: a name, price, photo, and the shop you can buy this product at. This data is constantly updated. Google Shopping has rather complicated guidelines & policies that may need some meditative digesting, but it is usually cheaper than AdWords.
Plus, this October, right before the caravan of holidays, Google announced a new AdWords feature — Showcase Shopping ads. Showcase Shopping ads let you group together a selection of related products and present them together to introduce your brand or business. These ads help the user decide where to buy when they search for more general terms:

You will need to upload your products into Google Merchant Center and create a Shopping campaign in Google AdWords. A starting point is here. If you want to give it a serious try, please read this guide first.
To proceed with Google AdWords Showcase Shopping ads, take a look here.
5. Hotel ads
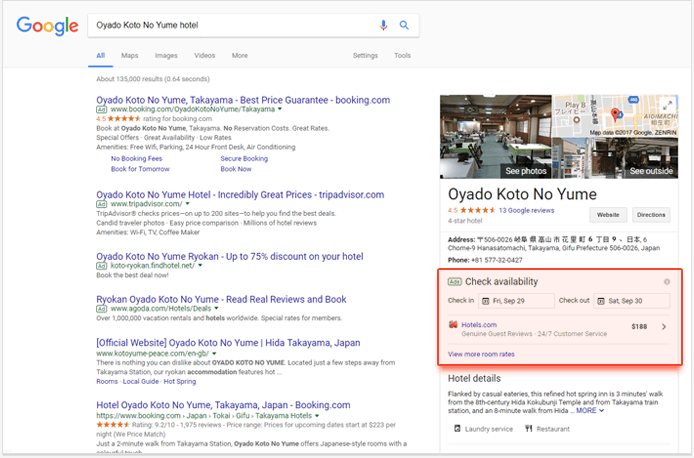
As part of branded Knowledge Graph listings for hotels, Google often displays in-card options to book a room right from the SERP. The providers of the rooms can include both the hotels’ official websites and booking companies. Google gets either pay-per-click or a commission which is charged when bookings are made via listings on Google.
Start with Google Hotel Ads by choosing an authorized integration partner, who can set up and manage your Google Hotel Ads campaign, or contact Google’s team and they will help you to find a suitable one.
Travel boxes.
6. Route box
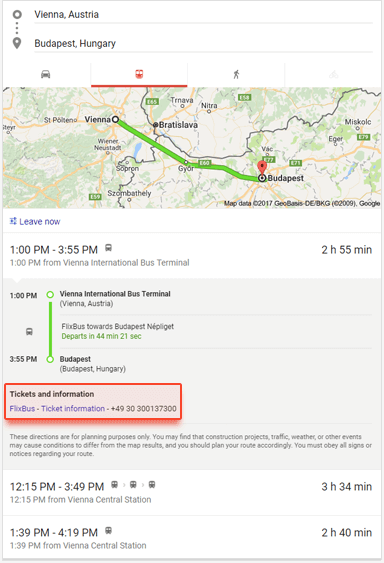
When Google believes that the searcher is looking for a way to get from one place to another, it often shows a Route box, with a map and directions for driving, walking, cycling as well as train and bus schedules. You can see the same results on Google Maps when searching for a route.
As soon as you switch to the public transport tab and click on one of the routes, you will receive the information about the transportation company plus a link to its website, a link to the ticket information, and a phone number. A big chocolate candy — getting listed with the Route box is free for transportation companies.
If you are a transportation service that operates with fixed schedules and routes, you can join Google’s free transit partner program.
7. Google flights
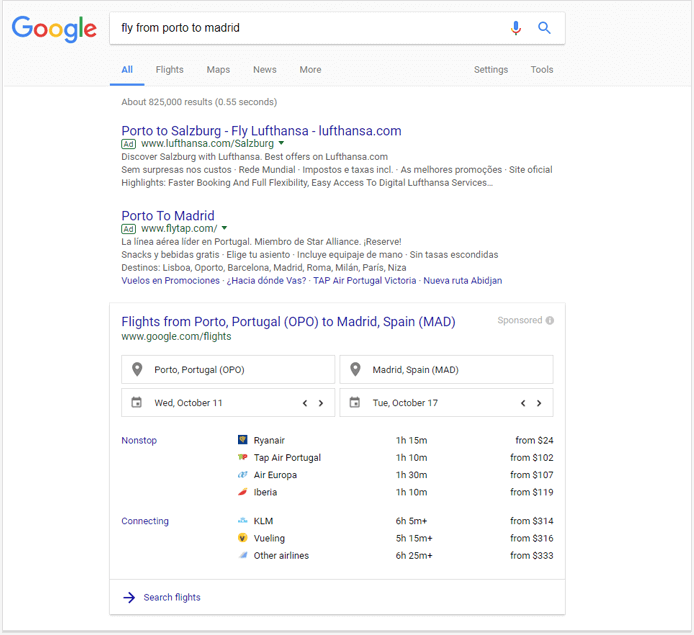
Google Flights was born in 2011 as a result of Google’s purchase of ITA matrix software, a powerful tool that lets searchers discover flight schedules and rates through Google search. The Flights box includes the names of airlines/travel agencies with links to their websites, duration of flights, and fares.
Clicking the “Search flights” link will take you to the Google Flights page, where you can pick a suitable flight and book it quickly. Google gets a commission from merchants for these sales. In some cases, you can purchase a ticket without even leaving Google.
There is no option to sign up to be listed on Google flights. Instead, you can contact ITA to be considered.
Local results.
8. The local pack (the 3-pack)
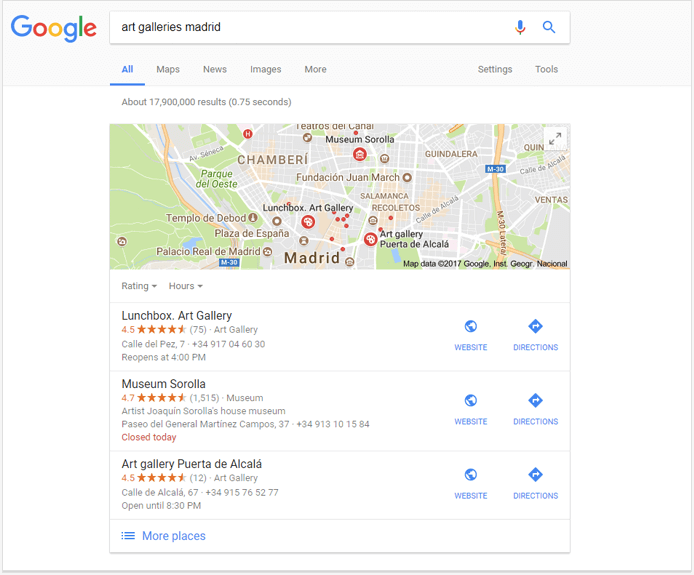
Local packs in Google are now comprised of a map and 3 listings. The three listings that we see depend largely on their location; when you click on one of them, it takes you to Google Maps with an extended view of this business.
1. Claim your Google My Business listing.
Google takes most of the info for local business listings (including an address, phone number, images, map, etc.) from that page. Once you have set up your profile, make sure to:
- Add a long, unique description with a link to your official website;
- Choose the correct category for your business;
- Upload a high-resolution profile image and cover photo;
- Double check your address, local phone number, and opening hours;
- Update the information when necessary.
2. Gain positive reviews.
The reviews from your Google My Business page can play a big part in your listing’s prominence in local search, as the overall review rating is included into a local pack snippet. Plus, Google has an option for searchers to select only those businesses that are above a certain rating. Try to encourage your happy customers to make reviews for your business on Google, for example, you can offer some harmless incentives for reviews.
If you need more tips, we have them right here.
9. Local Knowledge Graph panel
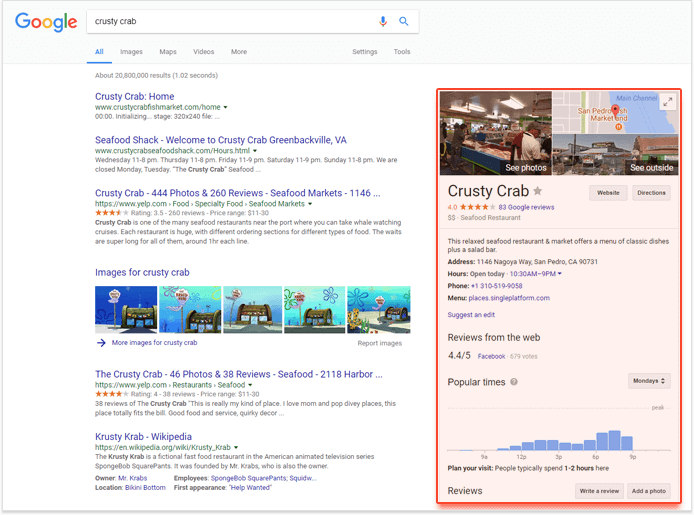
Google usually displays a local Knowledge Graph for branded queries that imply that the searcher is looking for a business in a particular location, not the overall information about the company. This listing is kind of a doppelganger of a branded Knowledge Graph, but it does not draw the data from the same sources.
A local Knowledge Graph usually includes:
- a picture;
- a map with a pin;
- a link to the company’s website;
- a link to Google Maps for directions;
- a Google review score;
- a business type;
- a short description;
- contact details;
- a Popular Times graph for some niches;
- a few excerpts from Google reviews;
- a “People also search for” section.
Amusingly enough, brands can have both the branded and local Knowledge Graph displayed for a search query:
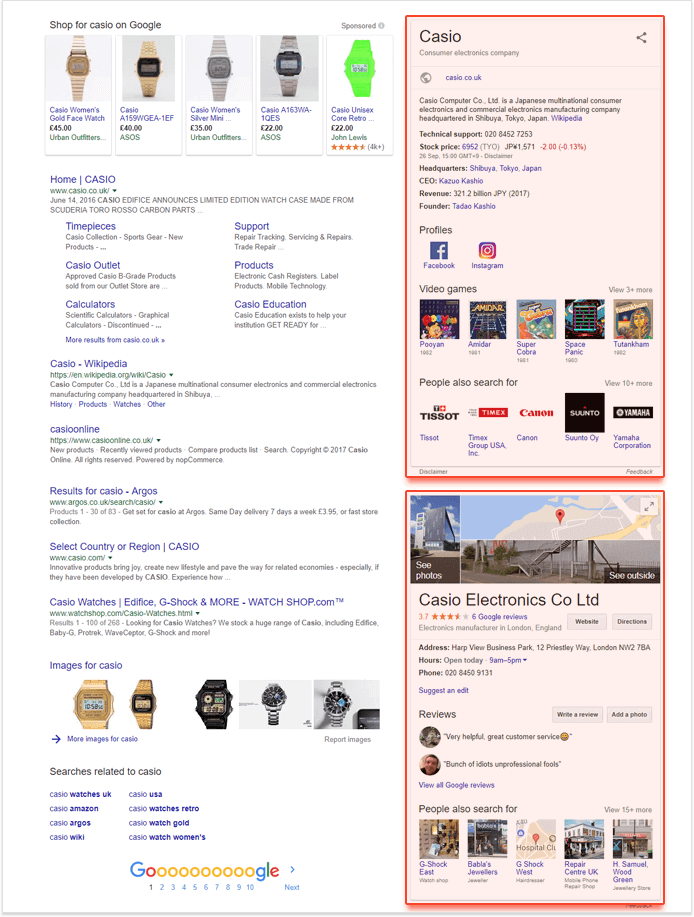
1. Set up a Google My Business page.
A Google My Business account is a must if you need to gain a local Knowledge Graph listing. Make sure to provide correct and relevant information: an address, map, contact details, and opening times. Plus, pick a quality preferred photo. This photo can’t be a logo and should represent your business. Opt for a square picture, 250×250 pixels or larger.
2. Do a citation campaign.
Make sure your business is mentioned in all relevant local & industry specific directories. For example, Yelp and TripAdvisor for restaurants, Booking.com and TripAdvisor for hotels, etc. Double check your data for consistency across all these listings. It will make you look more prominent and credible in Google’s googly eyes.
3. Get positive reviews.
Google loves reviews and loves to include them anywhere it is suitable. Try to get at least 5 reviews on Google — you will be rewarded with the yellow review stars placed under your company name. If you see a happy customer, try to persuade them to leave a review, raise their eagerness to do so by offering some benign incentives. Here you can check out Google’s guidelines for reviews.
Featured snippets.
10. Rich answer
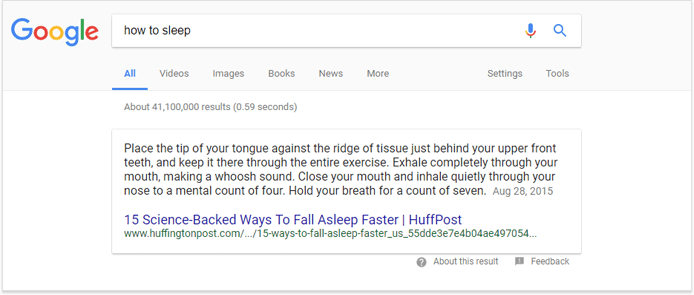
The types of featured snippets, being so many, are worth a separate blog post, but it makes more sense to focus on those that are of SEO value and are able to bring real traffic. Those are mostly text-only answers. While some of the rich answers pop up as Knowledge Graphs (without a link), most of them come from the third-party sources and do include a link to the website.
If your page gets a featured snippet, it can give you a massive traffic boost, as the link to your website will be above search result number 1 (so the CTR will rocket).
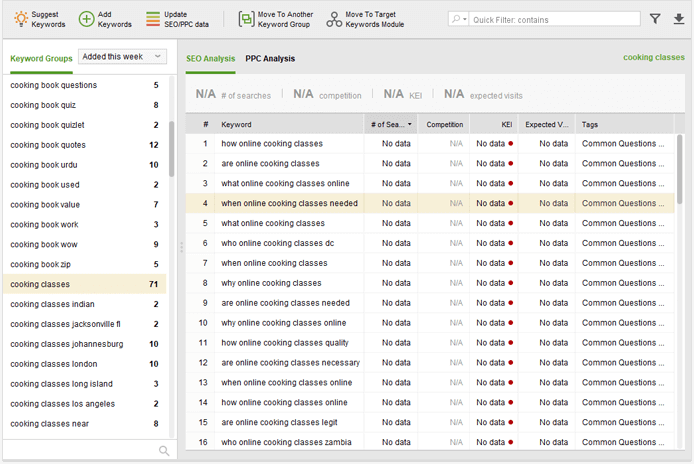
1. Discover questions which you can build your content around.
You can do it efficiently with the SEO PowerSuite Rank Tracker‘s Common Questions keyword research method. Go to the Keyword Research module and click Suggest Keywords. Select the Common Questions method, paste your seed keywords, and, as a result, you will receive tons of suggestions related to your keywords:
2. Directly answer the question in your content.
Try to include the question and a concise, direct answer to it. The structure is very important here. Google can pick up properly tagged paragraphs, lists, and tables from your content (or make its own lists from your headings!). Make answers explicit in your content; if your content is long-form, include a short TL;DR version with a question-answer pair.
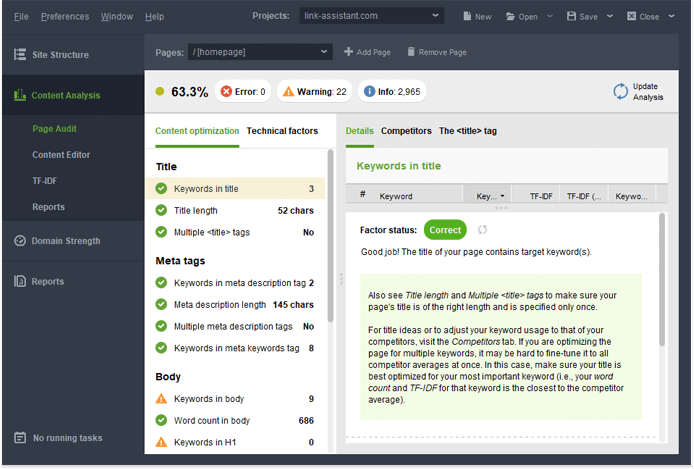
3. Optimize the page.
Let’s do some on-page SEO. First of all, make sure to include your keywords and related terms in your content. You can do the analysis and optimization with SEO PowerSuite’s Website Auditor. The tool’s content editing module will give you specific optimization advice and recalculate your optimization scores as you type.
Bonus: here is a more detailed guide of how to get a featured snippet.
11. People also ask
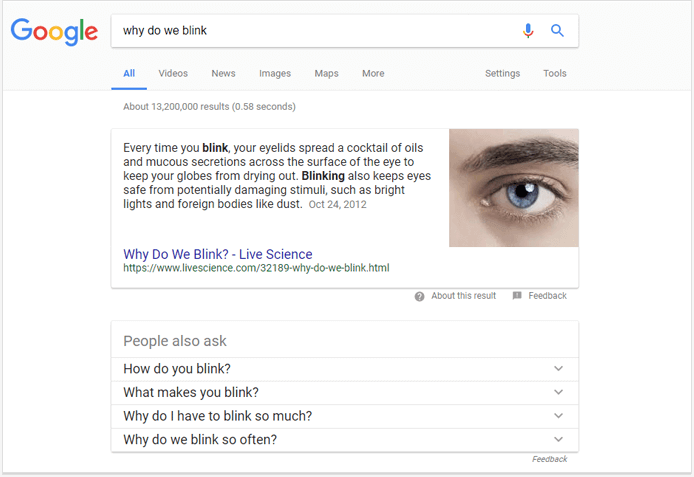
The People also ask (PAA) box is a Google universal SERP result that answers questions related to the searcher’s initial query. Let’s treat it as a close relative of the featured snippet.
I have often seen PAA boxes right under the featured snippet, but now they are kind of on their own — PAAs can actually appear all over the first page of search results.
Each PAA box contains 1 — 4 related questions which you can expand to reveal answers that Google has pulled from other websites — they look exactly like featured snippets. You can see the website’s URL under the answer plus a “Search for” link that leads you to a Google SERP of this particular PAA question.
Moreover, this PAA box has a dynamic nature — when you click a PAA question, the box expands and shows more questions. It can take you to infinity — it is able to show a few hundred PAA questions. Though, according to different studies, including the one by STAT (check out also the updated stats), after some expanding, questions start to repeat.
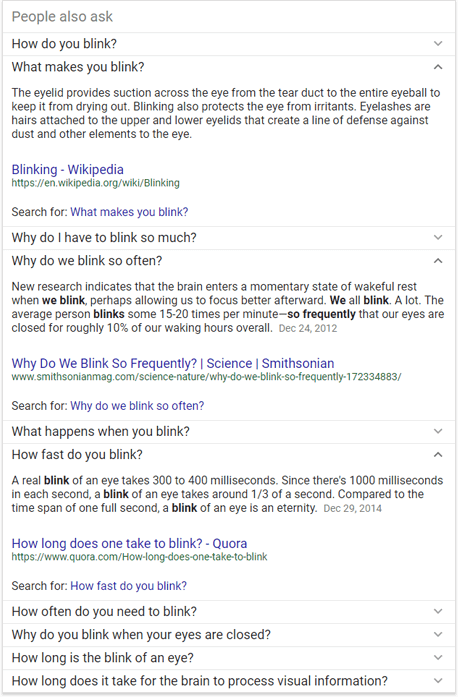
Where do these questions come from? It seems that nobody knows for sure. Certainly not from the featured snippets, as many PAA questions do not return a featured snippet if you follow a link to the prospective SERPs. Some think that they are based on a Machine Learning algorithm. It may be true, as some questions do not look natural (for example, grammatically). The same study by STAT showed that a third of the analyzed PAA questions returns zero search volume, so they are not selected from the questions that the searchers usually ask.
In spite of being all mysterious, the PAA box has a very lucrative nature and can bring you a good deal of traffic. The questions that seem more prominent tend to repeat during that dynamic PAA box expanding, and the same questions mostly return the answers with the same source, i.e. PAA question/answer combos stick together. So if you have earned a spot in the PAA box, it can pay off multiple times. There are also occurrences when a single URL can answer different, yet topical, PAA questions.
The evidence above about the repeated question-answer combos proves that once Google finds a trusted source, it sticks to it. Thus, the optimization goes around suitable questions and great content, exactly like for featured snippets:
-
- Discover questions to build your content around.
- Give direct and concise answers in your content and structure them properly (in this case, PAAs are usually paragraphs or lists).
- Optimize your content for keywords and related terms.
Plus!
- Dive into the infinity of dynamic PAA box expansion for the topics related to your industry for new ideas both for your questions and your content.
12. Featured video
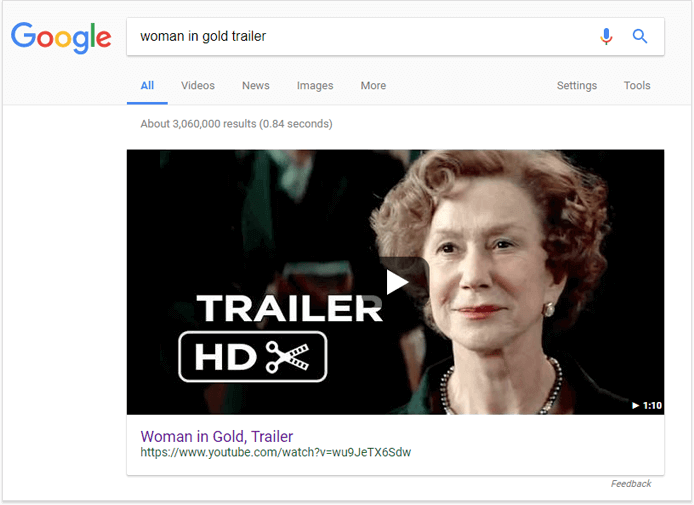
When you Google your favorite song or a movie trailer, you can see a large embedded video above all the search results. However, it does not work (or works really rarely and it is hard to spot) for other possible video results. While music videos contain, besides a URL, at least some information on the album, artist, genre, and sometimes drop-down suggestions on “People also search for”, other video snippets contain just a URL. Plus, you can watch a video right on the SERP. The video snippet may also appear together with the Knowledge Graph panel.
A positive thing for possible traffic is that the link will lead you not necessarily to the official source of the video, as it has been before, but to the third-party sources. So we can cautiously think that Google is willing to give this search result space to non-official sources of videos that are uploaded to YouTube.
As it is not that clear how Google chooses which video source to snip and due to the limited range of currently snippable video content, there are no sure ways to get there. However, Google can shift towards developing this feature and include all kinds of video content. You know, at the beginning, this search result appeared only for music videos, now it pops up with ease for movie-related video content. Thus, if you want to be ready in case this feature evolves, there are some tips to stir your knowledge on the video marketing techniques:
-
- First of all, if you do not have a YouTube account, get it. All the observable large video snippets are pulled from YouTube.
- Optimize the title and meta description of your videos for keywords. Do not overdo it, though.
- Make sure that your videos are formatted to be played and conveniently viewed from any device (a desktop, phone, tablet, etc.)
- Publish your videos both on your website and your YouTube channel. You can also publish them on social networks for better exposure.
- Submit a video sitemap, so that Google could find all the videos from your site.
- You can consider displaying the name of your website or brand right on your video (in a subtle way). Remember, non-music large embedded videos are displayed on the SERP just with a link. So if the searchers watch it right on the search results page, they will have no idea where this video comes from. But the mention of your website name on the video can catch their eye:

- If your industry is not music- or movie-related, you can create how-to videos that explain how to do anything in your line of business. This will show your expertise that can rank for a particular topic. There can be also interviews, a video series of some process, reviews, etc.
Organic search results.
13. Regular organic results
Do some good old SEO. First, theory, then practice! Educate yourself about SEO to understand the optimization flow. Then make sure to get some full-cycle SEO tools that will help you to save time and make the optimization more comprehensive.
14. Rich snippets
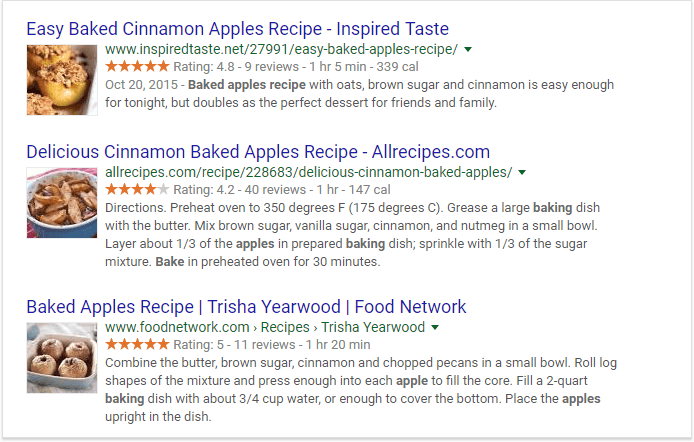
The days when the regular organic listings all looked the same are gone for good — the structured data markup has crept in and added some attractive, “calling for clicks” visualization.
Classic Google listings all look the same till you use some markup to enrich your SERP snippets with images, ratings, and other industry-specific pieces of data (in addition to the classic title, URL, and description).
Thanks to Google, you don’t have to be a web developer if you need to mark up the structured data on a website. You can use Structured Data Markup Helper. Before adding the schema markup chunk of HTML to your pages, remember to preview your snippets by copying and pasting your page’s source code into Google’s Testing Tool.
15. Videos
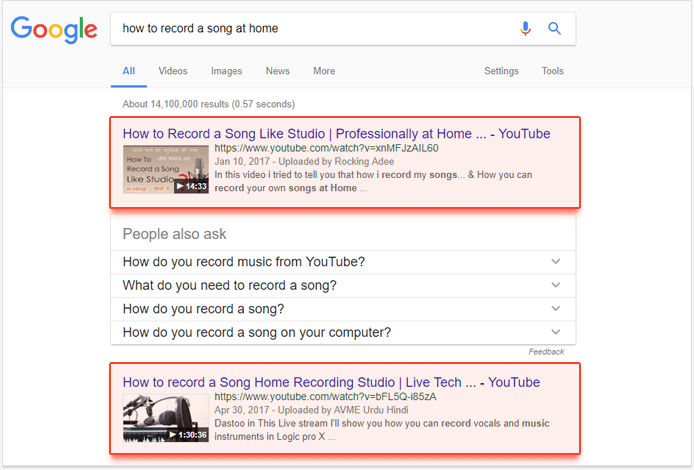
Video results are integrated into organic results and have a customized snippet. They consist of a thumbnail of the video, a publication date, and the name of the video channel. If multimedia content is a key strategy of your marketing campaign, then you have to think of the techniques to leverage your video results in Google.
1. Create video content.
If you are new to video marketing, YouTube is a great start. How-to videos and video reviews do best on this platform. Think of the industry-related topics you could address and produce videos to cover them.
2. Optimize your video’s file name, title, description, and tags.
The first thing you need to optimize is the file name of your video for uploading: it should be concise, clear, and keyword-oriented. The same about the video’s title (plus, remember, it should be attractive enough to be clicked). Putting your keyword at the beginning of the title is considered a best practice. As for your video’s description, remember to include a link to your site at the top of it. Ideally, the description should be 200+ words long and clearly state what your video is about.
3. Mind user experience.
Comments, thumbs up, and bounce rates are the factors that both Google and YouTube consider when determining videos’ quality. You can see user experience stats in YouTube Analytics to spot areas you can improve.
4. Promote your videos.
Social media exposure is good for both traffic to your videos and your Google ranks. Distribute your videos on social media, Quora, industry forums, and embed them in blog posts to gain views and comments.
Vertical search results.
16. Images
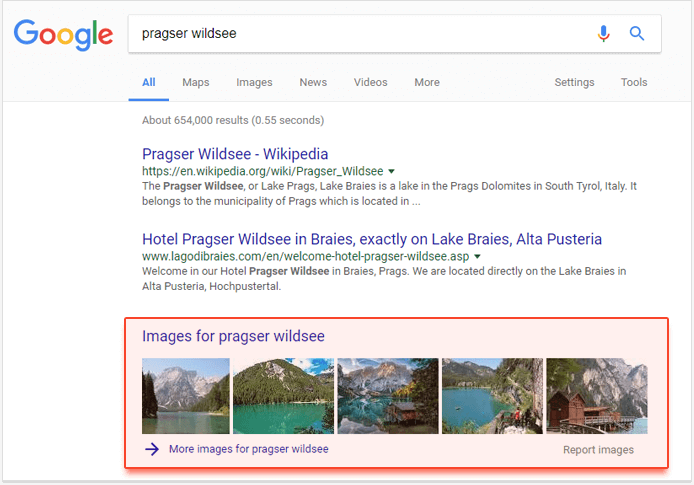
Image result boxes are often seen in Google’s organic SERP and appear on the first results page, now often in its lower part due to the abundance of other kinds of search results, like Carousels, News, Things to do, etc. These results link directly to Google Images.
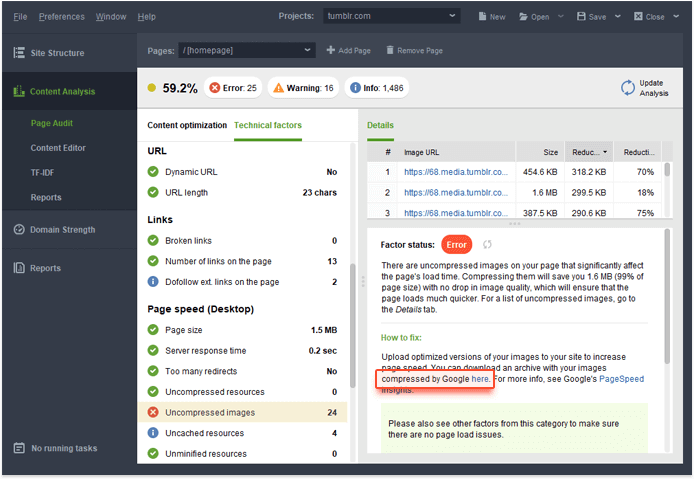
1. Optimize image size.
Google loves to be speedy, so your images should be as small as possible while maintaining their visual aesthetic. You can check your images and get a ready download link for their compressed version if their size can be safely reduced in SEO PowerSuite’s WebSite Auditor. Go to Content Analysis -> Page Audit, switch to Technical factors and click Uncompressed Imagesunder the Page Speed section. Download your readily compressed images:
2. Use unique, original images only.
For obvious reasons, Google seldom ranks multiple copies of the same image. For images that appear across several sites, they’ll do all they can to dig out the original version of the image and include it in the search results.
3. Do not forget about image titles and alt attributes.
Image titles and alternative attributes help Google to understand what your picture means, so try to use those tags to make Google understand. If relevant, include your target keywords in both the title and alt text.
4. Optimize your page content and URL.
Google analyzes the webpage as a whole to determine the relevancy of images to queries. So make sure to include your keywords in your content and URL and optimize your page fully. You can do it with WebSite Auditor‘s Content Analysis module.
17. Social listings
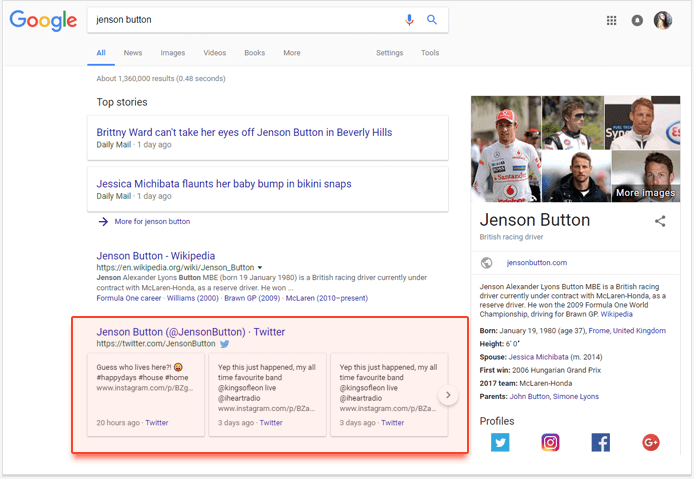
For now, social listings on the first SERP are represented only by Twitter, but it may change in the future — social results have been evolving a lot over the past years. In the current layout of Twitter listings, you can click through the account’s recent tweets without leaving Google.
1. Use schema markup for organizations on our homepage.
You see, not a step without structured data markup — it is incredibly useful for all kinds of Google listings. A fine solution for higher rankings on Google is to use organization markup on your homepage.
2. Have your social account verified.
Google is more likely to discover social profiles if they are verified by the social networks. Here are some great tips for verifying your profiles.
18. Google news
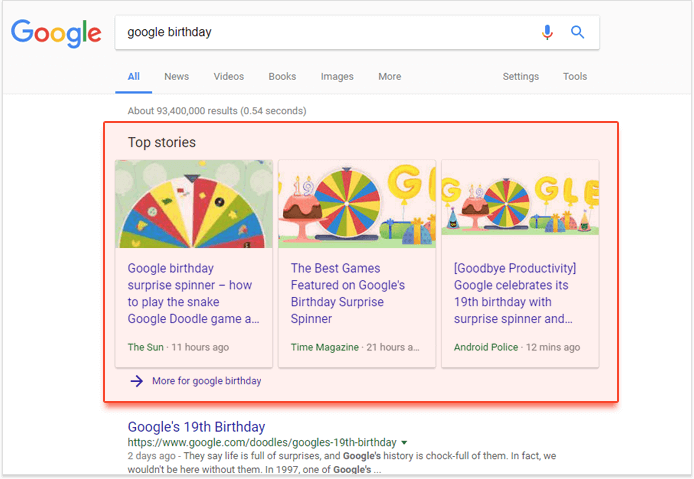
Google News “Top stories” result blocks appear when in response to queries, Google is able to find some related news posts. Such results usually appear all over page 1 of the search results and have up to three links. The links can be enhanced with a thumbnail image.
If content creation is a key part of your marketing strategy and you consider your content newsworthy, you can become a publisher for Google News. To understand whether you are credible enough, check Google’s guidelines for news sites. The main requirement is that your content should be of high quality, fresh, unique, and non-promotional.
Alternatively, you might want to consider offering your content to be re-published by bigger publishers that already have an established presence on Google News. A good starting point is searching Google News for your industry terms to note the most frequent contributors.
Phew… That was exhaust..exciting! It is amazing how quickly search result types are evolving. Google is definitely into experimenting.
So what search result types have brought some traffic to your site? Have you discovered any new types or their varieties? I’m looking forward to more exploring!